본문
Atomic-scale sensing of the magnetic dipolar field from single atoms
by Prof. Andreas J. Heinrich (heinrich@ewha.ac.kr
)
Department of Physics
Director of Center for Quantum Nanoscience, Institute for Basic Science
Understanding and controlling quantum systems at atomic level have promised incredible potential to utilize them for ultra-sensitive quantum sensors and quantum information processors. In conventional spin resonance experiments, electromagnetic radiation interacts with an ensemble of 107 to 1010 spins to achieve magnetic imaging. In recent years, there have been notable progresses in detecting and coherently controlling individual atomic-scale spin centers such as nitrogen-vacancy center (NV) at diamond [1]. However, positioning the individual spins and characterizing weak spin-spin interactions with sub-nanometer precision have remained outstanding challenges.
The scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) enables us to position individual spin with atomic precision and has been highly useful to study the spin states and spin excitation of atoms and molecules [2]. In the magnetic sensing, the magnetic dipole-dipole interaction is essential for structural imaging of materials and bio-molecules but its use is currently limited by ensemble measurements. Although STM experiments can study atom-by-atom interaction, the dipole-dipole coupling energies of atoms are too small to be detected by the STM.
In this research, we successfully combine the superior energy resolution provided by electron spin resonance (ESR) with capabilities of STM [3], to measure magnetic dipole-dipole interactions in precisely controlled atomic arrangements of magnetic atoms on surfaces. On artificially built assemblies of magnetic atoms (Fe and Co) on a magnesium oxide surface, we measure that the interaction energy between the ESR sensor (Fe) atom and a nearby atom shows an inverse-cube distance dependence (r −3.01±0.04). This demonstrates that the atoms are predominantly coupled by the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction when atom separations are greater than 1 nm. Using the dipolar sensors, magnetic moments and positions of individual atoms can be determined with high accuracy. The achieved atomic-scale spatial resolution in remote sensing of spins may ultimately allow the structural imaging of individual magnetic molecules, nanostructures and spin-labelled biomolecules.
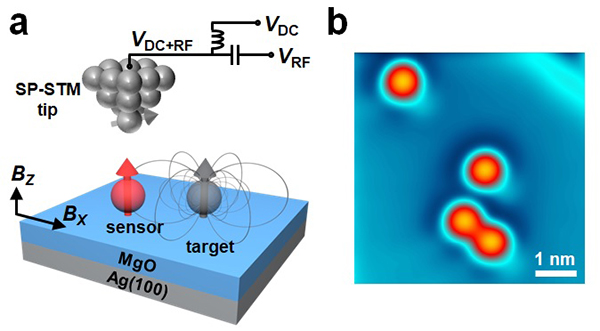
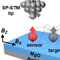
Figure 1. Experimental set-up for ESR-STM. a, Schematic of sensing dipolar field from a target atom. Electron spin resonance of individual Fe atoms on MgO/Ag(100) is driven by high radio-frequency electric field at the STM tunneling junction. b, Constant-current of STM image of four Fe atoms (V=0.1V, I=10pA, Bz=0.18T, Bx=5.7T, and T=1.2K).
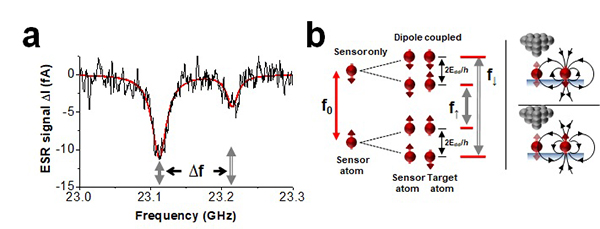
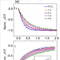
Figure 2. Magnetic dipole-dipole interaction. a, ESR spectrum (black curve) of an Fe atom when another Fe atom is positioned ~2.46 nm away. The two spectral peaks correspond to the two magnetic states of the nearby atom because each state of the nearby atom generates a different local magnetic field at the sensor atom. b. Schematic of the energy levels of the sensor atom, modified by its dipole-dipole interaction with the target atom.
* Related Article
Taeyoung Choi, William Paul, Steffen Rolf-Pissarczyk, Andrew J. Macdonald, Fabian D. Natterer, Kai Yang, Philip Willke, Christopher P. Lutz* & Andreas J. Heinrich*, Atomic-scale sensing of the magnetic dipolar field from single atoms, Nature Nanotechnology vol.12, 420–424, 2017
[1] H.J. Mamin et al., Nanoscale nuclear magnetic resonance with a nitrogen-vacancy spin sensor, Science 339, 557 (2013).
[2] A.J. Heinrich et al., Single-atom spin-flip spectroscopy, Science 306, 466 (2004).
[3] S. Baumann et al., Electron paramagnetic resonance of individual atoms on a surface, Science 350, 417 (2015).