본문
Development of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Tailored Mobile Intervention for Nurse Burnout

by Prof. Chiyoung Cha
College of Nursing
PURE Research Profile
chiyoung@ewha.ac.kr
Nurse burnout leads to an increase in turnover, which is a serious problem in the healthcare system. Although there is ample evidence of nurse burnout, interventions developed in previous studies were general and did not consider specific burnout dimensions and individual characteristics.
This study aimed to develop and optimize the first tailored mobile intervention for nurse burnout, which recommends programs based on artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, and to evaluate its usability, effectiveness, and satisfaction.
The tailored mobile intervention for nurses, Nurse Healing Space, consisted of a 4-week program, with the 2-week program repeated twice. The program included mindfulness meditation, laughter therapy, storytelling, reflective writing, and acceptance and commitment therapy. The AI algorithm recommended one of these programs to participants by calculating similarity through a pretest consisting of participants’ demographics, research variables, and burnout dimension scores measured using the Copenhagen Burnout Inventory. The AI identified the recommended program as effective if the user’s burnout score decreased after completing the 2-week program and updated the algorithm accordingly (Fig 1).
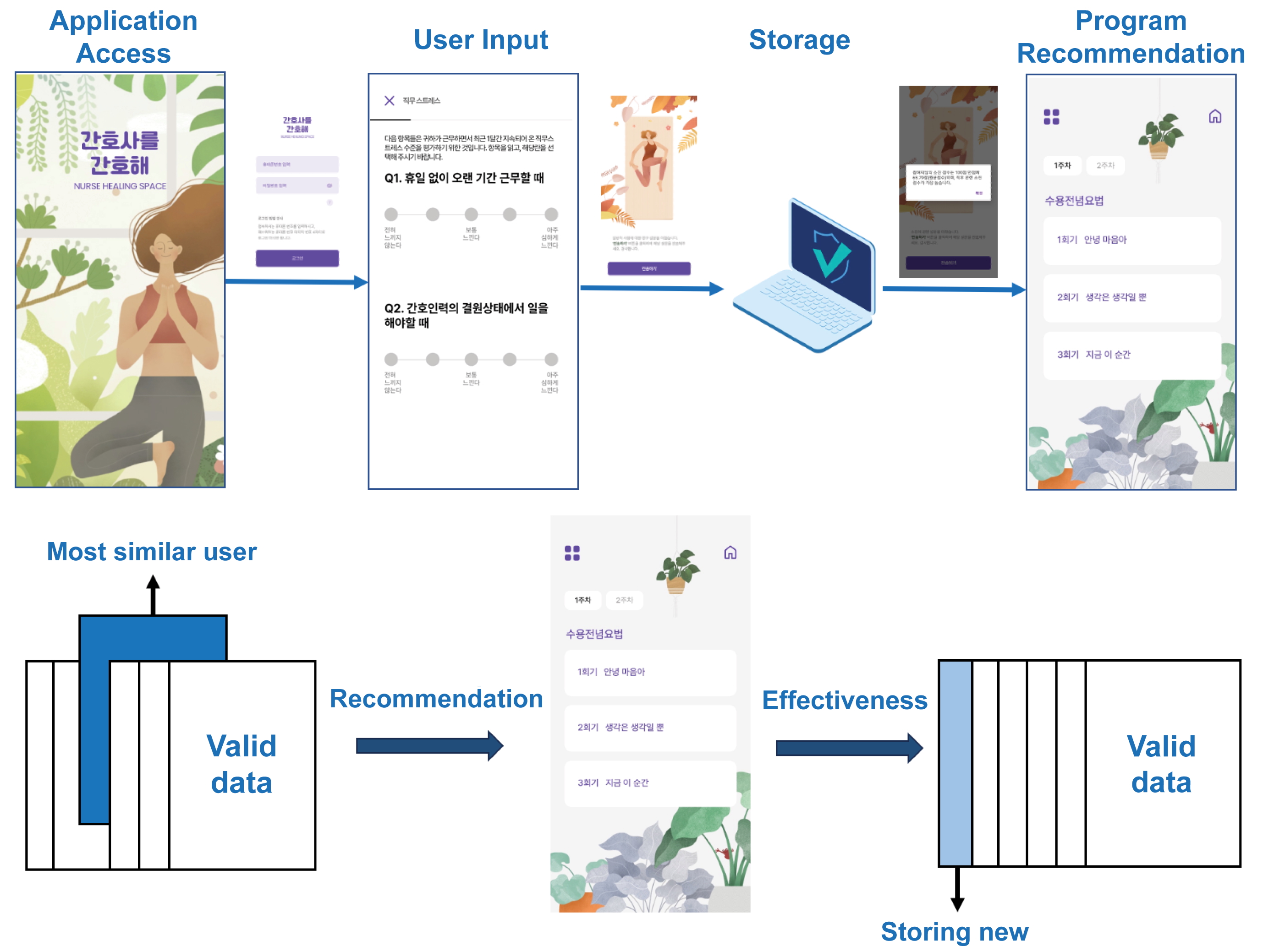
Figure 1. Nurse Healing Space operation.
We measured burnout, job stress, stress response (using the Stress Response Inventory Modified Form), app usability, coping strategy (using the Coping Strategy Indicator), and program satisfaction (1: very dissatisfied; 5: very satisfied) after the 4-week program. We conducted a pilot test (n=10) and then optimized the AI for n=300 participants. A paired 2-tailed t-test, ANOVA, and Spearman correlation were used to evaluate the intervention's effectiveness and the optimization of the algorithm.
Nurse Healing Space was implemented as a mobile app equipped with a system that recommended 1 program out of 4 based on similarity between users through AI. The AI algorithm effectively matched the recommended program to the most similar participants based on valid data. The convenience and visual quality were good, but the lack of notifications and program customization made users unhappy. Nurses’ burnout scores decreased significantly after the completion of the first 2-week program (t=7.012; p<.001) and reduced further after the second 2-week program (t=2.811; p=.01). After completing the Nurse Healing Space program, job stress (t=6.765; p<.001) and stress responses (t=5.864; p<.001) decreased significantly. During the second 2-week program, the burnout level reduced in the order of participation (r = –0.138; p = .04). User satisfaction increased for both the first (F=3.493; p=.03) and second programs (F=3.911; p=.02).
Nurse Healing Space, the first customized burnout reduction intervention for nurses, highlights the potential of AI-based systems to provide tailored solutions for different burnout types. Nurse managers can use such programs to reduce nurse turnover rates, improve patient safety and quality of care, increase employee satisfaction, lower costs, and enhance the overall efficiency of the healthcare system.
* Related Article
Aram Cho, Chiyoung Cha, Gumhee Baek, Development of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Tailored Mobile Intervention for Nurse Burnout: Single-Arm Trial, JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INTERNET RESEARCH, Vol. 26, e54029, June 2024