본문
Mass Transport Control by Surface Graphene Oxide for Selective CO Production from Electrochemical CO2 Reduction
By Prof. Jonggeol Na (jgna@ewha.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science
Electrochemical CO2 reduction is always accompanied by a competitive hydrogen evolution reaction as water is used as a hydrogen source. In addition to intrinsic activity control, geometrical factors of electrocatalysts such as their porous structure have been demonstrated to affect the reaction selectivity, but understanding its origin is still important. Herein, we demonstrate that reduced graphene oxide layers can effectively control the Faradaic efficiency for CO production of porous zinc nanoparticle electrocatalysts. Simply tuning the coverage of graphene oxide dramatically varies Faradaic efficiency for CO production from 66 to 94% even in the bicarbonate electrolyte at the same biased potential, in which the hydrogen evolution rate was notably suppressed without sacrificing CO2 reduction to CO production rate unlike many Zn-based electrocatalysts. The graphene oxide layers are revealed to play roles in providing geometric barriers for the mass transport channels of reactants rather than changing the chemical states of the Zn-based electrocatalysts according to in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopic analysis and electrochemical reaction kinetic studies. In addition, computational fluid dynamics simulation studies estimate the Faradaic efficiency dependence on the surface coverage and suggest that the selective suppression of H2 evolution is associated with the larger increment in local pH compared to that in local pCO2 at the porous electrocatalyst surfaces. Decoupling between these reactant concentrations is originated from the higher consumption rate and lower bulk concentration of proton compared to those of CO2, and the surface coating with graphene oxide can be an effective way to control mass transport channel.
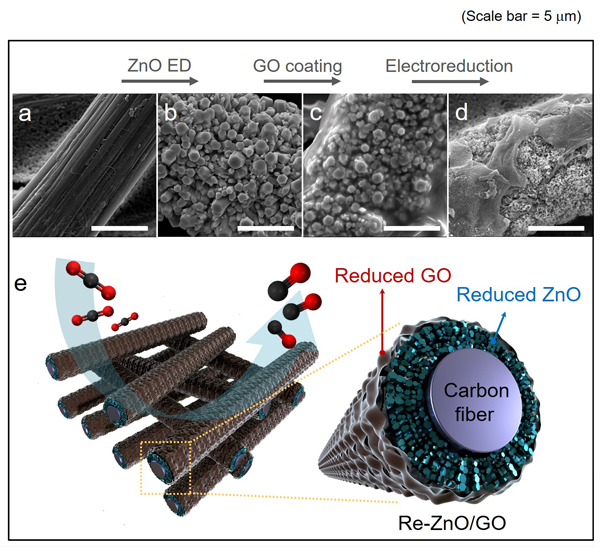

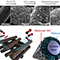
Figure 1. The synthetic procedures of R-ZnO/rGO electrodes are composed of ZnO electrodeposition, GO coating, and electroreduction. SEM images of (a) one fiber of carbon paper, (b) electrodeposited ZnO on carbon paper, (c) ZnO/GO, and (d) R-ZnO/rGO. Scale bar, 5 μm. (e) Visualization showing the detailed structure of R-ZnO/rGO electrodes.
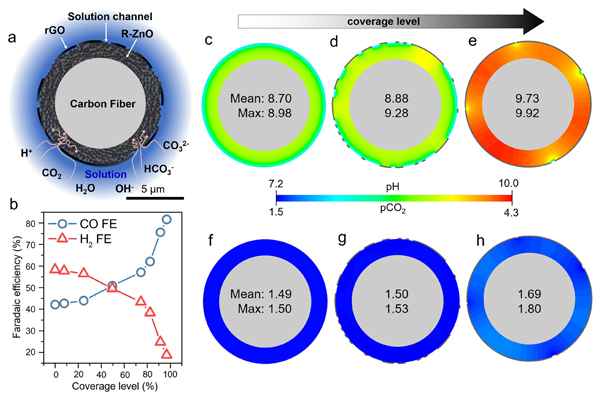
Figure 2. Computed local pH and reduced GO coverage effects. (a) Schematic of computational fluid dynamics simulation domain. (b) Plots of CO FE and H2 FE as a function of coverage level. Contour plots of (c–e) pH and (f–h) pCO2 under a steady state at different coverage levels of 0, 50, and 97.5%, respectively.
* Related Article
Nguyen, D. L. T., Lee, C. W., Na, J., Kim, M. C., Tu, N. D. K., Lee, S. Y., ... & Hwang, Y. J. (2020). Mass transport control by surface graphene oxide for selective CO production from electrochemical CO2 reduction. ACS Catalysis, 10(5), 3222-3231.