본문
Perovskite-based photodetectors: materials and devices
by Prof. Dong Ha Kim (dhkim@ewha.ac.kr)
Department of Chemistry and Nano Science
While the field of perovskite-based optoelectronics has mostly been dominated by photovoltaics, light-emitting diodes, and transistors, semiconducting properties peculiar to perovskites make them interesting candidates for innovative and disruptive applications in light signal detection. Perovskites combine effective light absorption in the broadband range with good photo-generation yield and high charge carrier mobility, a combination that provides a promising potential for exploiting sensitive and fast photodetectors that are targeted for image sensing, optical communication, environmental monitoring or chemical/biological detection. Currently, organic-inorganic hybrid and all-inorganic halide perovskites with controlled morphologies of polycrystalline thin films, nano-particles/wires/sheets, and bulk single crystals have shown key figure-of-merit features in terms of their responsivity, detectivity, noise equivalent power, linear dynamic range, and response speed. The sensing region has been covered by ultraviolet-visible-near infrared (UV-Vis-NIR) to gamma photons based on two- or three terminal device architectures. Diverse photoactive materials and devices with superior optoelectronic performances have stimulated attention from researchers in multidisciplinary areas. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the recent progress of perovskite-based photodetectors focusing on versatile compositions, structures, and morphologies of constituent materials, and diverse device architectures toward the superior performance metrics. Combining the advantages of both organic semiconductors (facile solution processability) and inorganic semiconductors (high charge carrier mobility), perovskites are expected to replace commercial silicon for future photodetection applications (Figure 1).
Recently, Prof. Dong Ha Kim and Dr. Huan Wang at Ewha Womans University summarized a comprehensive review paper of extensive research results focusing on the perovskite-based photodetectors. They systematically reviewed both materials and various techniques towards high-performance perovskite-based photodetector. Perovskites can be implemented by a relatively simple process with containing high charge mobility, which is, therefore, soon to be capable of replacing commercial silicon and is expected to be a promising material for next generation optoelectronics.
NOTE: This work has been selected as a front cover paper in the issue of Chemical Society Review (Figure 2).
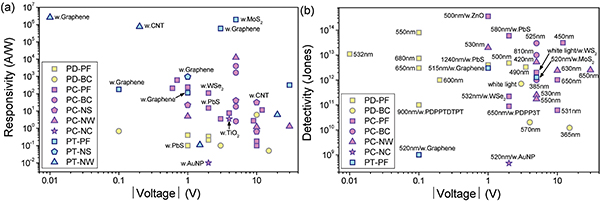
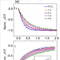
Figure 1. Plots of responsivity versus voltage (a) and detectivity versus voltage (b) for different architecture devices based on diverse perovskite materials. Phototransistors based on hybrid perovskite-1D/2D conducting materials and photoconductors based on high-quality perovskite crystals show the high responsivities in figure a. Photodiodes and photoconductors can achieve high detectivities with the low and high working voltage, respectively, and the corresponding detection wavelength is shown in figure b. PD, photodiode; PC, photoconductor; PT, phototransistor; PF, polycrystalline film; BC, bulk crystal; NS, nanosheet; NW, nanowire; NC, nanocrystal.

Figure 2. Front Cover of the journal of the Chemical Society Review (Vol. 46, page 5204-5236).
* Related article
Huan Wang, and Dong Ha Kim*, Perovskite-based photodetectors: materials and devices, Chemical Society Review, 2017, 46, 5204–5236